
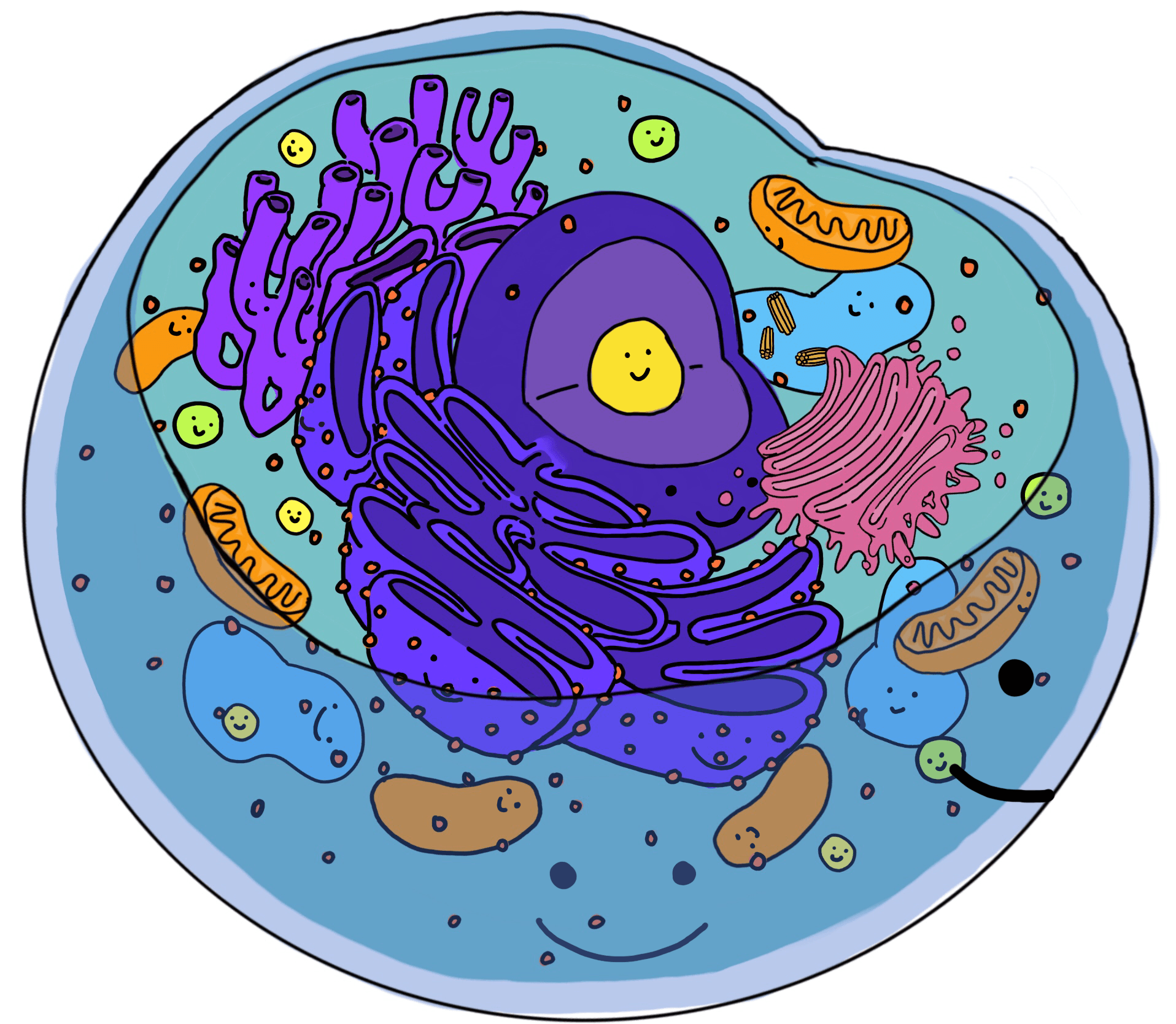
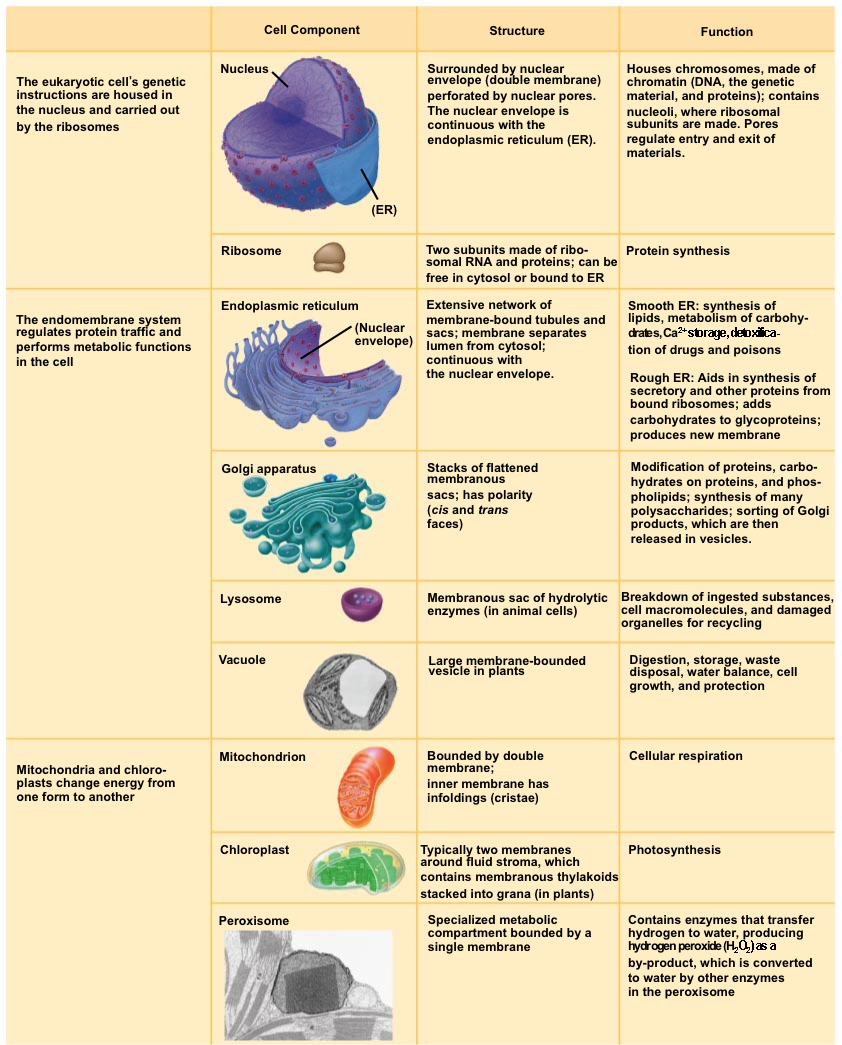
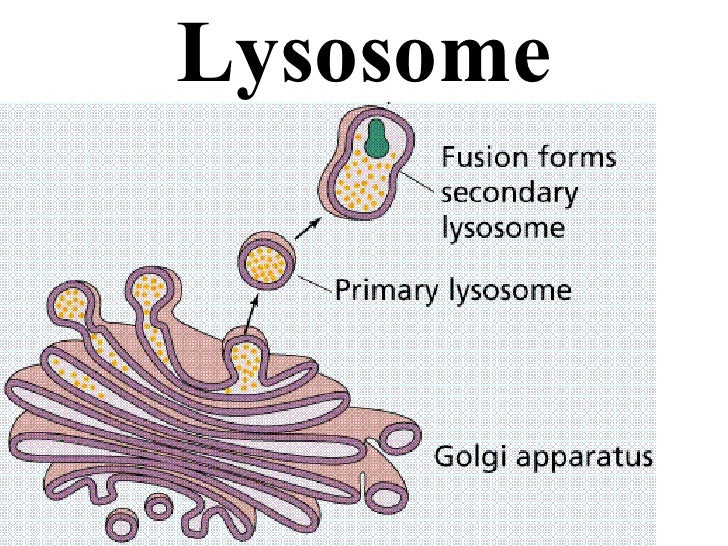
To fuel daily life & growth, the cell must… take in food & digest it take in oxygen (O2) make ATP (energy) remove waste Organelles that do this work… cell membrane vacuoles lysosomes mitochondria ATPġ1 Cell Membrane Boundary of the cell Made of a phospholipid bilayerĮmphasize word parts here: phospho= phosphate head lipid= fatty acid tail bi= 2ġ2 Cell membrane (ctd.) separates cell from outside environment Explain that the colors are added digitally to enhance the different parts.ġ0 1st MAJOR FUNCTION: CELLS NEED TO MAKE ENERGY! Rigid, protective and supportive barrier Located outside of the cell membrane Porous Made from fibers of carbs and proteins Plant Cell Walls are made from Cellulose Plasmodesmata: holes or channels in the cell wall that allow for transport/communication This is an actual microscopic image. Intermediate filaments also provide structural support.ĩ Cell Wall Found in plant and bacterial cells Microtubules mostly move organelles around the cell. Helps the cell with movement Microtubules Microfilaments Actin, also found in muscle cells, mainly help maintain cell shape in their cytoskeletal role. Most high school textbooks, however, use the word “cytoplasm” to mean “cytosol.”Ĩ Cytoskeleton Acts as skeleton and muscle Provides shape and structure The correct use of each term is shown here. You may or may not wish to distinguish between cytosol and cytoplasm. Lots of different ones found in eukaryotic cells Cytoplasm is a thick, liquid residing between the cell membrane holding all living material inside the cell doesn't contain the nucleus. CO2 out take in & digest food make energy ATP build molecules proteins, carbs, fats, nucleic acids remove wastes control internal conditions respond to external environment What are they responding to? build more cells growth, repair, reproduction & development ATPħ Cell Organelles Carry out specialized functions within the cell No membrane bound organelles genetic material not in the nucleus Cell membrane Small Eukaryotes (YOU!) Have organelles Genetic material contained in nucleus Largeĥ Categories of cells Prokaryotes Eukaryotes Bacteria animal cells Van Leeuwenhoek first to view cells under the microscope Schleiden plants made of cells Schwann animals made of cells Virchow new cells only come from division of other cells ALL THESE SCIENTISTS LED TO THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE CELL THEORY!ģ Cell Theory All living things are composed of cellsĬells are the basic units of structure and function in living things New cells are produced from existing cellsĤ Cell Categories Prokaryotes Eukaryotes (YOU!)
–Ģ Scientists of Cells Hooke viewed cork coined the term “cells” Run through the entire presentation before using it in class so that you know what’s coming next! It helps to print the outline and notes to have with you while presenting so that there are no surprises. Use this presentation in conjunction with the Cell Organelle note-taking worksheet.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
